 Many of you might have noticed that while you see the properties of some folder their are two sizes shown over there in properties window. Those sizes are labeled as “Size” & “Size on disk”. You can also notice that size on disk is always greater than actual size. So, here is the explanation of these two terms.
Many of you might have noticed that while you see the properties of some folder their are two sizes shown over there in properties window. Those sizes are labeled as “Size” & “Size on disk”. You can also notice that size on disk is always greater than actual size. So, here is the explanation of these two terms.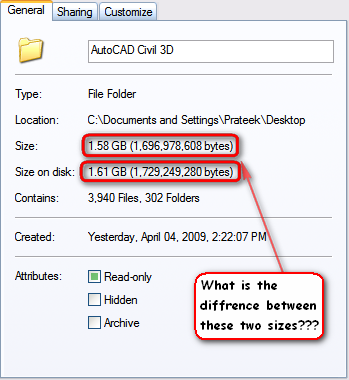
- Size – It is sum of sizes of all containing files and folders in it, in raw form (count of number of bytes).
- Size on disk – It displays the effective size which they occupy in disk.
It is the file system of hard disk which determines the “Size on Disk”, where as “Size” will remain same, irrespective of file system (like NTFS, Fat32, UDF, etc.).
The disk is further divided into tracks and sectors, file system determines how many tracks or sectors to be included in one cluster. So, if the disk is having a cluster size of 16KB (generally in case of FAT file system). Any file on that disk will have size on disk in multiples of 16KB. So, a file size up to 16KB will occupy 16KB as disk space and file from size 16 to 32KB will occupy 32KB on disk space and so on.
In this way a large volume of disk space gets unused. So, there is a need of file system having smaller cluster size. This is one reason Microsoft came up with a new file system NTFS, after windows millennium.
Related: Accessing Linux partitions from Windows OS
[Editors Note: This post is by our co-blogger Prateek from Go Hi-Tech where he writes about Technology.
If you too like to write for Devils Workshop, please check this. Details about our revenue sharing programs are here.]
3 Comments
i guess NTFS and FAT has its own advantages and disadvantages.
sometimes fat is better than ntfs.
nice post about a simple concept
It means only size on disk matter